What is Task Manager in Windows? what do you know about this nice tool that was found on your windows in this article we will know everything about it and how to use it so let’s start.

Table of Contents
Toggle1. What is task manager in Windows?
Task Manager, formerly recognized as Microsoft Windows Task Manager, serves as an integral component within the Windows operating system (OS). It empowers administrators and end users alike to effortlessly oversee, control, and address various tasks. In the realm of Task Manager, a task can encompass anything from an application and a Windows process to a background process—each representing a fundamental unit of programming under the OS’s purview.
Task Manager aids IT professionals in swiftly pinpointing potential system bottlenecks, and addressing performance or stability issues proactively. It facilitates the detection of unusual behavior, signaling potential malware or unauthorized software.
Task Manager empowers administrators with the ability to terminate applications and processes, fine-tune processing priorities, and optimize computer performance by setting processor affinity. Moreover, it provides insights into currently logged-in users, allowing administrators to troubleshoot login or connectivity issues efficiently by disconnecting users as needed.
2. How can we use Windows Task Manager?
Task Manager, in Windows OS since NT, evolves with Microsoft’s continuous updates, enabling administrators and power users to achieve significantly more than the original version allowed. Windows provides multiple ways to open Task Manager, such as the following:
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Del and select Task Manager on the Windows Security screen.
- Right-click the taskbar, and choose Task Manager.
- Right-click the Start button, and opt for Task Manager.
- Type task manager in the Windows search box and click the app in the results.
When you open Task Manager, you’ll see a simple view listing the apps currently running. This view doesn’t include Windows or background processes.
Switching from the compact view, users can expand Task Manager by clicking the More Details option at the window’s bottom. This expanded interface unlocks all Task Manager features. Power users and administrators will likely navigate here most often.
The default tab is Processes, but users can change it. Once expanded, the view remains unless they return to compact before closing. To switch back, click Fewer details at the window’s bottom.
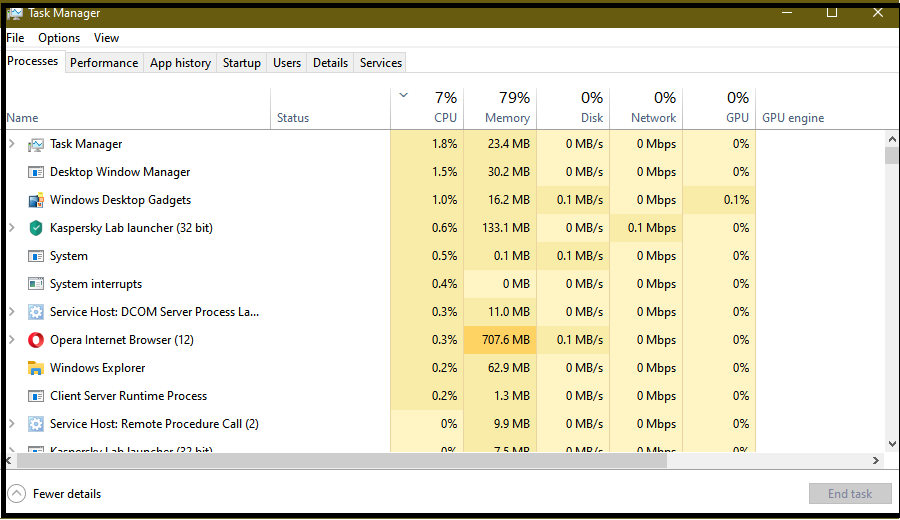
Tabs in expanded view display varied info on system apps, Windows, and background processes. Tabs may differ by OS. Windows 11 Task Manager, similar to Windows 10. Both feature a UI with seven tabs:
- The Processes tab displays live processes on the system, grouped into Apps, Background, and Windows. Users can view them categorically or as a list, and perform various operations like ending tasks or exploring details on the Details tab.
- The Performance tab visually tracks real-time hardware resources. To check specific resources, select them in the sidebar—typically CPU, Memory or ram, disk or SSD, and network. The GPU resource may also appear. Users can launch Resource Monitor from this tab.
- The app history tab shows CPU and network usage per process for the current user and system accounts. Initially displaying Universal Windows Platform apps, users can opt for all processes. Data is time-specific, starting from the listed date. Users can delete history and restart data collection.
- The startup tab lists processes that load during computer boot. Users can enable or disable a startup process.
- The user’s tab displays resource utilization and process info for connected users. Similar to the Processes tab, data is grouped by individual users. Users can perform operations like ending processes or disconnecting listed users from the system.
- The details tab shows all current processes like the Processes tab but provides additional information like session ID, CPU time, memory details, priority, handles, threads, and I/O reads/writes.
- The services tab, a streamlined version of the Services utility, lists actively running services. Users can start, stop, or restart services and access the full Services utility.
Tabs display data in tables similar to the Processes tab. Users can sort data by columns and choose additional columns to display. Options related to each process are also accessible. The Performance tab stands out, offering real-time visualizations for various hardware resources, like CPU performance or memory performance.
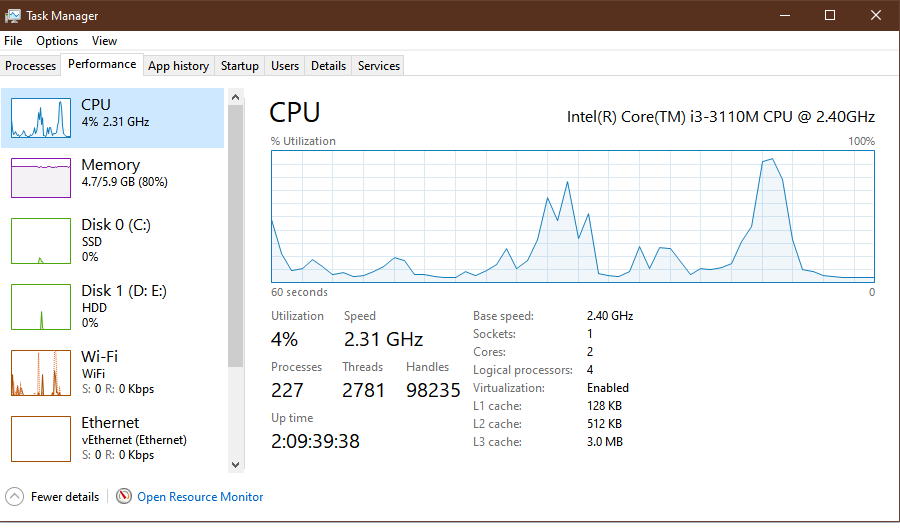
Windows 11 Task Manager specific. Windows Server Task Manager resembles Windows 10 and 11 UI but lacks the App history and Startup tabs. While Task Manager has improved, it remains a basic tool without advanced monitoring capabilities. For features like alerting and comprehensive reporting, IT teams should opt for more in-depth tools like Microsoft Process Explorer.
FAQs

Q1 Is Task Manager only for advanced users?
Not at all! Task Manager is designed for users of all levels. Its user-friendly interface caters to beginners while offering advanced features for power users.
Q2 Can I disable startup programs without using Task Manager?
While there are other methods, Task Manager provides a straightforward way to manage startup programs, making the process hassle-free.
Q3 How often should I check Task Manager for system performance?
Regular check-ups are beneficial. Monitoring Task Manager can help you identify and address performance issues before they become major problems.
Q4 Are there any risks in ending processes using Task Manager?
Ending processes should be done judiciously. Closing essential system processes may lead to instability. Exercise caution and research unfamiliar processes before termination.
Q5 Is Task Manager available in all versions of Windows?
Yes, Task Manager is a built-in feature in all modern versions of Windows, from Windows 7 to the latest releases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Task Manager is the unsung hero of Windows, empowering users to take control of their system’s performance. Whether you’re troubleshooting issues, optimizing startup, or monitoring resource usage, Task Manager is the Swiss Army knife every Windows user needs.
Finally, I hope my article added some valuable information to you. IF you have some questions? Let me know in the comments below. I’ll try my best to answer them.




