Do you always listen to a word called Gpu? Is that right what does GPU mean? In this article you will learn everything about the graphic processing unit so let’s start this new tech article.

Table of Contents
Toggle1. What does GPU mean?
GPU stands for graphic processing unit it is a computer chip capable of rapidly performing mathematical calculations to render graphics and images GPUs find applications in both professional and personal computing endeavors. Initially designed for rendering 2D and 3D images, animations, and videos, GPUs have now expanded their utility to a broader spectrum of tasks.
Similar to a central processing unit (CPU), a GPU serves as a vital chip component within computing devices. However, a notable distinction lies in the GPU’s specialized function: it is purposefully crafted to efficiently manage and enhance graphics tasks, facilitating the seamless display of graphical content on various devices like PCs and smartphones.
An electronic device with a GPU can render 3D graphics and video, ideal for gaming and visual applications. Technological advancements have made GPUs more versatile, and utilized in creative content, video editing, HPC, and AI.
2. What does GPU do?
In the early days of computing, the CPU bore the burden of performing calculations essential for graphics tasks, encompassing the rendering of 2D and 3D images, animations, and video. However, the emergence of increasingly graphics-intensive applications strained the CPU, leading to a decline in overall computer performance.
To address this challenge, GPUs emerged as a solution to relieve CPUs of graphics-related tasks. By executing graphics calculations rapidly and in parallel, GPUs facilitate swift and seamless content rendering on computer screens. With the GPU handling these calculations, the CPU is liberated to manage all other non-graphics-related operations.
3. How does GPU work?
GPUs operate through parallel processing, leveraging multiple processors to handle distinct segments of a task simultaneously. Additionally, GPUs feature dedicated RAM called VRAM tailored to accommodate the substantial volume of data processed, particularly in graphics-intensive scenarios.
In graphics applications, the CPU communicates instructions to the GPU for rendering graphics content on-screen. The GPU executes these instructions in parallel and at rapid speeds, facilitating the display process known as the graphics or rendering pipeline.
4. What are the uses of GPU in our days?
GPUs have become integral to PC gaming, ensuring seamless, high-fidelity graphics rendering. Their versatility extends beyond their original design, thanks to enhanced programmability. This evolution has led to GPUs being utilized in diverse fields, including accelerating AI workloads and facilitating machine learning (ML). the applications of GPUs include:
- Real-time rendering of 2D and 3D graphics applications.
- Video editing and content creation.
- Enhancing video game graphics.
- Accelerating ML tasks like image recognition and facial detection.
- Training deep learning neural networks such as Chatgpt and another AI example
Moreover, GPUs have found utility in cryptocurrency mining, particularly for Bitcoin and Ethereum. Their ability to execute rapid, parallel mathematical calculations makes them indispensable for such endeavors, a capability conventional laptops with regular CPUs lack.
5. What are types of GPU?
We have 2 types of Gpu:
- integrated GPU
- Discrete GPU
Integrated into the computer’s motherboard or CPU, GPUs save space and decrease power consumption. While reducing cost, they limit upgradability. Modern gaming laptops meet game requirements, delivering smooth graphics and immersive experiences.
Discrete GPUs, also known as dedicated GPUs or VGA cards, are typically mounted on separate circuit boards. These powerful graphics cards are designed for resource-intensive tasks like 3D gaming. While they offer increased processing power and upgradability, they consume more energy and generate significant heat, often requiring dedicated cooling systems for optimal performance of both the GPU and the laptop.
6. What is Cloud GPU?
Cloud GPUs offer an alternative to traditional deployments, ideal for heavy computing tasks like machine learning or 3D visualizations. They eliminate the need for local GPU hardware and software, providing flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. Users can access a variety of GPU types on demand via web browsers for diverse applications, from gaming to data analysis. Google Cloud and other providers offer high-performance GPU options tailored to different workloads and budgets.
7. Difference between Gpu and Cpu?
GPUs can be integrated with CPUs on the same circuit, either on a graphics card or the motherboard. While CPUs handle fundamental computer instructions, GPUs specialize in rapidly rendering high-resolution images and video. In essence, CPUs handle the majority of a computer’s commands, whereas GPUs excel in complex mathematical and geometric calculations, particularly for graphics rendering and other computationally intensive tasks.
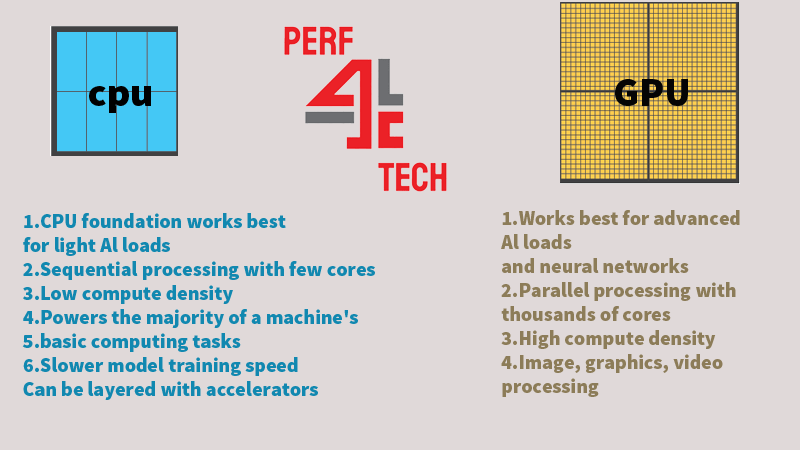
Processors come with varying numbers of cores and transistors. Cores act as individual processors within the main processor, capable of handling tasks independently. While CPUs have fewer cores and process tasks sequentially, GPUs boast hundreds or thousands of cores for parallel processing, enabling rapid graphics output.
Single-core CPUs lack parallel processing ability, unlike multicore CPUs. GPUs typically have more transistors than CPUs. CPUs boast higher clock speeds, making them more suitable for basic computing tasks.
8. Are GPU and Graphics cards the same?
While GPU and graphics card are often used interchangeably, they have distinct differences. The GPU serves as a specific unit within the graphics card, responsible for image and graphics processing. Conversely, the graphics card is responsible for presenting images to the display unit.
FAQ

Q1 What is GPU vs RAM?
Video memory, located on the graphics card or GPU, is distinct from the computer’s Random access memory (RAM). It is purpose-built to efficiently manage the high bandwidth requirements of graphics-intensive applications.
Q2 Is A GPU better than a CPU?
The CPU manages tasks necessary for server software to operate smoothly, while the GPU assists by handling concurrent calculations. Unlike the CPU, the GPU excels at quickly processing simple, repetitive tasks by breaking them down into smaller components and executing them in parallel.
conclusion
In conclusion, the GPU, or Graphics Processing Unit, is a specific unit within a graphics card responsible for image and graphics processing. It works in tandem with the graphics card, which presents images to the display unit.
Finally, I hope my article added some valuable information to you. IF you have some questions? Let me know in the comments below. I’ll try my best to answer them.




