What are the most common errors that will destroy your motherboard? Experiencing a malfunction in any computer component can be highly inconvenient for users, potentially impeding the full operation of the device. Whether it’s an issue with the operating system, processor, graphics card, RAM, or computer screen, imagine a malfunction affecting all these components simultaneously! Yes, we’re referring to malfunctions related to the motherboard in this article we will know everything about these errors and how you can avoid them so let’s start.

As the board that interconnects all computer components, motherboard malfunctions are among the most serious computer issues. Unlike a single replaceable component to address the problem, motherboard problems require special attention. Manufacturers typically prioritize the motherboard’s quality, implementing various protective measures against potential risks. Despite this, the inherent risks of improper use and user practices remain significant threats, potentially leading to irreparable damage. Let’s delve into the most common improper practices that can harm the motherboard in computer systems, possibly resulting in complete failure.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. What are the most common errors that will destroy your motherboard?
Numerous reasons can lead to motherboard malfunctions, but the majority of issues with computer motherboards, and the most common ones are as follows:
- Short circuits in electronic and electrical circuits.
- Elevated temperatures.
- Sudden and significant voltage spikes during disconnection or connection.
- Incompatibility among electronic components and connected parts.
Computer motherboards typically come equipped with sufficient protection mechanisms to prevent the occurrence of the aforementioned problems. However, as we will explore in the following paragraphs, certain improper practices and mishandling of computers, operating them in unsuitable environments, and unprofessional disconnection/reconnection of motherboard components for replacing a faulty part or upgrading a component, can unexpectedly lead to such malfunctions and cause damage to the motherboard.
2. Neglecting proper ventilation and overheating
Elevated temperature poses as the primary adversary to electronic circuits, typically comprised of components inherently sensitive to heightened temperatures. Heat and electricity are intertwined elements, meaning the flow of electricity (electrons) in any electrical or electronic circuit is inevitably accompanied by the emission of heat. This results from the removal of electrons from the excited atoms of the material. The emitted heat leads to the heating of conductors and the substances constituting the circuit components. As the components of the circuit draw more electricity, the generated heat increases, working to raise the temperature of the circuit and its components.
Take the processor’s performance, for instance. When the computer is tasked with a simple operation that doesn’t demand high performance or consume data at high rates, such as web browsing, the device’s processor generates moderate heat. Conversely, in tasks requiring high performance, such as running modern video games or video editing software, the device’s processor needs to process a substantial amount of data. Consequently, it draws more electricity, accompanied by the generation of additional heat.
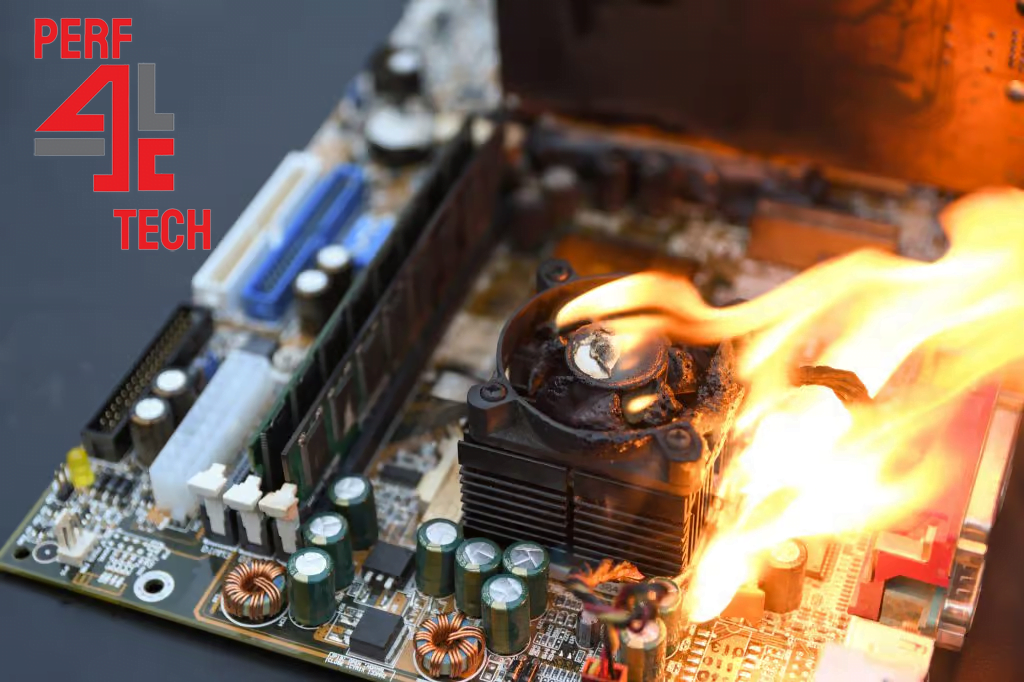
Most electronic components and chips utilized in computer electronic circuits are crafted from semiconductive materials, whose electrical conductivity increases with a rise in temperature until it reaches a critical value. Beyond this point, further temperature elevation inversely weakens their electrical conductivity, potentially leading to a complete loss of conductivity as the temperature continues to rise.
👉Used Computer Parts: What to Buy and Avoid.
Furthermore, elevated temperatures can induce increased mechanical stress on solder joints connecting motherboard components, accelerating their wear and tear. This results in cracks and fractures in these joints, compromising electrical connections. Therefore, it is imperative to maintain the temperature of motherboard components consistently below the critical threshold. This is where cooling fans and ventilation ports within the casing come into play—they consistently work to dissipate excess heat, ensuring the temperature of the device’s components remains within acceptable levels.

In rare instances, internal fans may fall short of effectively cooling the device components at rates sufficient to bring their temperatures down to safe limits. This can potentially harm the motherboard and even other hardware components connected to it. The risk factors escalate when dust and debris are present, occasionally leading to the obstruction of ventilation openings, especially when devices are used in hot environments, particularly during the summer.
It is, therefore, advisable to periodically clean ventilation ports. When a significant rise in the device’s temperature is observed, it is essential to inspect the fans, ensuring they operate optimally, providing adequate cooling rates, or replacing them with new ones if they are faulty. Additionally, caution should be exercised in using the device in an environment that allows for optimal ventilation whenever possible.
3. Failure to connect electrical cables and connectors correctly
At the outset of the article, we explained that a motherboard is essentially a board containing integrated electronic circuits that interconnect all computer components. It houses the cables and wires that facilitate the flow of electrical power from the power supply unit or PSU to the processor, its cooling fans, the graphics card, RAM, and other essential parts of the system.
Users often find the need to remove a component for maintenance, replacement in case of damage, or to upgrade to a newer version with superior specifications. During the reinstallation process after repair or when installing a new component, errors can occur. This might involve leaving a connection, cable, or screw dislodged or improperly connected on the motherboard. Additionally, the infiltration and accumulation of dust and debris within the motherboard’s slots and ports can hinder the secure installation of components, potentially leading to circuit malfunctions.
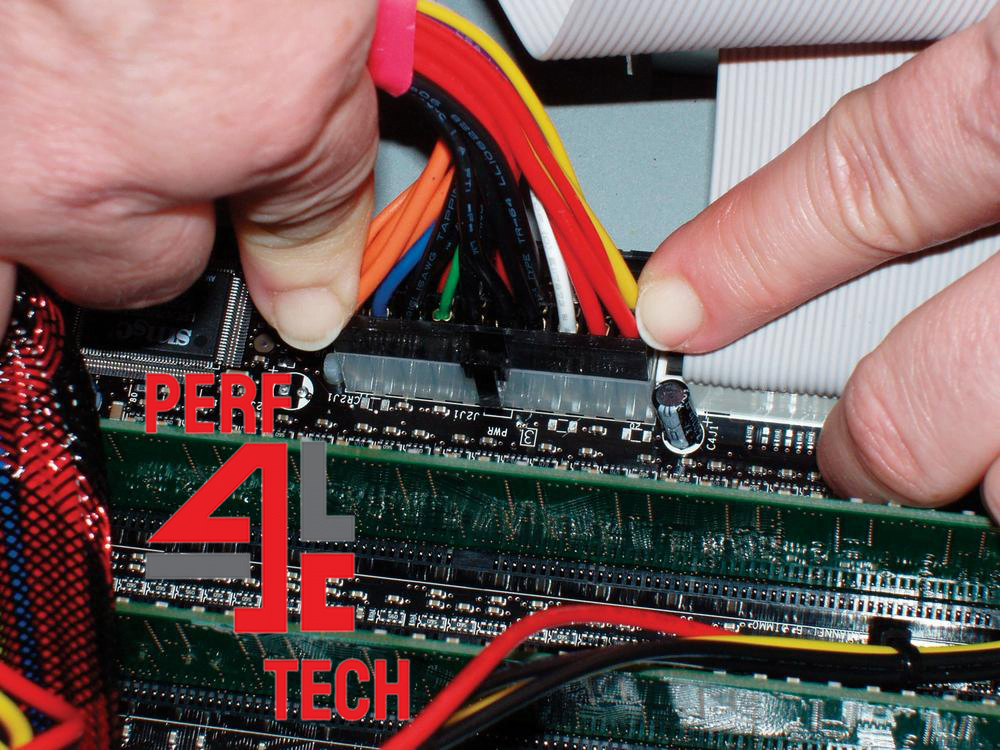
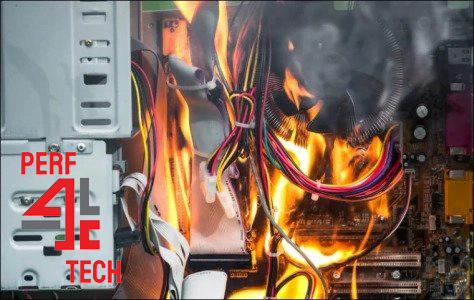
In general, electrical and electronic circuit short circuits refer to the passage of electric current along unintended paths due to the inappropriate proximity of conductors that should never come into contact. Short circuits are the primary cause of electrical malfunctions, commonly known as electrical shorts. In computer systems, a short circuit can result in component damage, sudden system shutdowns, and often lead to the motherboard catching fire, potentially damaging connected electronic parts.
Short circuits are rare in laptops but more prevalent in desktop computers, where numerous cables and connections are more susceptible to disconnection and reconnection during assembly, relocation, or component replacement.
To prevent motherboard short circuits, it is advisable to ensure the correct connection of all cables and motherboard components, securing all connections and firmly fastening screws after thoroughly cleaning the motherboard’s ports and slots from dust and debris. In case of computer startup failure due to a short circuit, examining the motherboard components, reinstalling parts, checking cable connections, and securely fastening them in their proper places is recommended. Also, verifying that all internal cables and wires are properly protected and insulated from each other with an outer layer of rubber or plastic is essential. Cleaning the mounting pins for electronic components and the dedicated ports is also advised, as dust accumulation can increase the risk of short circuits.
4. Touching motherboard components with electrically ungrounded hands.
All computer components, connected to the motherboard, require a specific electrical power draw to perform their functions. The power supply unit (PSU) plays a crucial role, pulling alternating current from the electrical outlet at a relatively high voltage (220 ~ 230 volts), transforming it into a steady direct current, and redistributing it to various computer parts at very low voltages tailored to their energy needs.
Household outlets can experience unstable voltages due to factors like electromagnetic fields and lightning. Sudden voltage spikes during device plugging and unplugging can affect electronic circuits, especially when high-power devices share the same line as computers. This can lead to brief surges in electrical flow and elevated voltages.
Static electricity on hands during maintenance may cause short-lived high voltage in motherboard cables. While voltage regulators in power supplies and motherboards aim to stabilize voltages, prolonged elevation can result in damage. To prevent this, avoid touching motherboard components without insulation, and minimize unplugging and reconnecting during operation. Using a surge protector at the electrical outlet is recommended to prevent sudden voltage spikes.
5. Try to use incompatible computer parts
When assembling or upgrading a desktop computer, compatibility issues between components can arise. For instance, using a power supply with insufficient capacity for the system’s needs can lead to motherboard failure and the inability to start the computer. Similarly, using high-heat-generating components without adequate cooling, like certain graphics processing units, can result in cooling system failure, elevated temperatures, and eventual damage to the components and motherboard. Additionally, the use of low-quality components, such as poorly manufactured RAM, can lead to complete system failure. Exercise caution when assembling a desktop computer, ensuring compatibility before adding or replacing any components.
Several websites, such as PCBuilder and PCPartPicker, can assist you in verifying the compatibility of your computer components. Additionally, ensure you purchase computer components that connect to the motherboard from reputable sources with a good reputation for delivering products of acceptable quality.
6. How to detect damage to the motherboard
Motherboards, like any other component, have a lifespan, and they can fail even without obvious signs. Unlike many other computer parts, motherboard issues are often challenging to detect, making it difficult to pinpoint them as the primary cause of system failure.
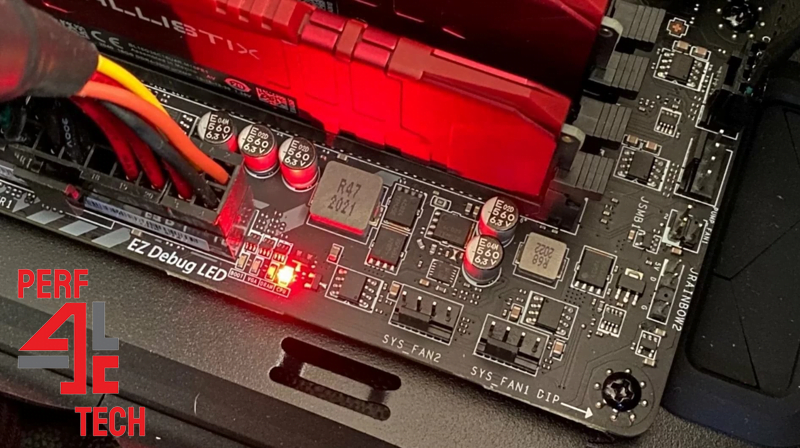
When facing problems like automatic restarts, sudden shutdowns, or device recognition failures, it’s not certain that the motherboard is at fault. To rule out other possibilities, the initial step involves disconnecting all components except the power supply. A green light from the power supply indicates its functionality and may suggest a faulty motherboard if absent. Testing with a different power supply on the same motherboard can help confirm if the issue lies with the motherboard.
If the power supply is fine, the next step is to check the processor and RAM. Connect them to the motherboard and attempt to start the computer. If the system doesn’t boot and initialize in the BIOS and UEFI settings, it indicates a potential issue with the processor, RAM, motherboard, or incorrect connection.
Reinstall the processor and RAM properly, and reset BIOS settings to default if possible, as incorrect configurations might cause issues. If the problem persists, check the CMOS battery connected to the motherboard responsible for BIOS operation. Although a faulty battery can disable the motherboard, it’s easily replaceable. Modern motherboards often have audible alerts and LED indicators for troubleshooting, but interpretations may vary by manufacturer. Seeking assistance from a specialized technician is advisable for identifying complex motherboard issues.
Finally, I hope my article added some valuable information to you. If you have some questions? Let me know in the comments below. I’ll try my best to answer them.




